The 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report – a study conducted by Ponemon Institute and published by IBM – recently revealed that the average cost of a data breach reached a record-high global average of $4.45 million USD – up 2.3% from 2022’s $4.35 million and 15.3% from 2020’s $3.86 million. The average cost per record also reached a new high of $165, up from 2022’s average of $164.
In its 18th consecutive year and a benchmark study in the security industry, IBM’s report provides IT, risk management, and security leaders with quantifiable data on root causes, consequences, and factors surrounding data breaches, as well as technologies that can be implemented to mitigate costs.
10 Key Findings from the Cost of a Data Breach Report
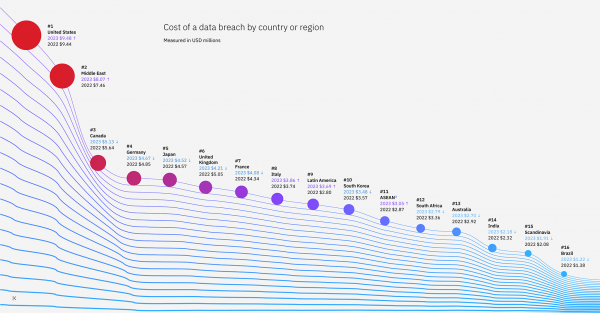 Highest Average Cost of a Data Breach by Country. For the 13th consecutive year, the United States topped the list for the highest average cost of a data breach at $9.48 million – an increase of 0.4% from last year’s $9.44 million. The Middle East had the second-highest average cost at $8.07M, up 8.2% from last year, while Canada, Germany and Japan finished the top five.
Highest Average Cost of a Data Breach by Country. For the 13th consecutive year, the United States topped the list for the highest average cost of a data breach at $9.48 million – an increase of 0.4% from last year’s $9.44 million. The Middle East had the second-highest average cost at $8.07M, up 8.2% from last year, while Canada, Germany and Japan finished the top five.- Costs of Data Breaches by Industry – For the 13th year in a row, the healthcare industry experienced the highest cost per data breach at $10.93 million, up 8.3% from last year and 53.3% over the past three years. Financial, pharmaceuticals, energy and industrial were also among the top five costliest sectors.
- Uncovering and Containing Breaches – It took an average of 204 days for organizations to identify a breach in 2023 and 73 days to contain the breach – compared to 207/70 days in 2022. The report showed that for breaches that took under 200 days to find and resolve, the cost was 23% lower at $3.93 million, while breaches over 200 days cost $4.95 million.
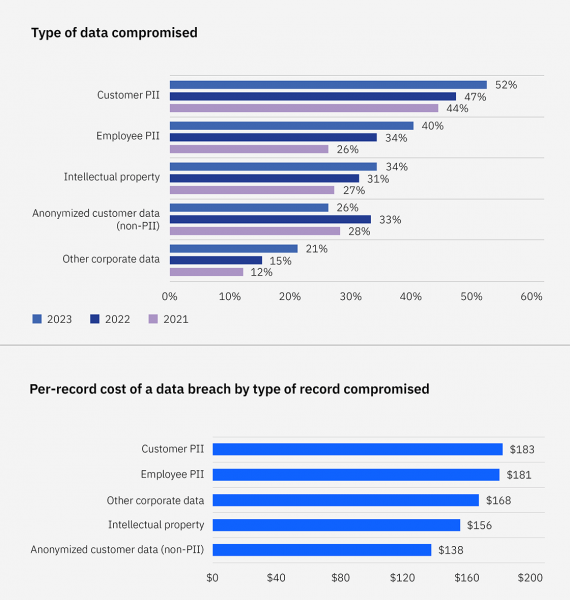 Customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII) – Customer PII data – names, Social Security numbers, credit card numbers – was the costliest type of data stolen in 2023, coming in at $183 per record. Not surprisingly, PII data was also the most breached record type, with 52% of all breaches involving some type of customer PII.
Customer Personally Identifiable Information (PII) – Customer PII data – names, Social Security numbers, credit card numbers – was the costliest type of data stolen in 2023, coming in at $183 per record. Not surprisingly, PII data was also the most breached record type, with 52% of all breaches involving some type of customer PII.- Initial Attack Vectors – Phishing was the most common initial attack vector for data breaches in 2023 – 16% of data breaches – and the second most expensive at $4.76 million per breach. Stolen or compromised records were the cause of 15% of breaches, costing $4.62 per breach, also taking the longest to contain at 328 days.
- Identifying Attacks – Breaches are identified in three ways – internally, by a third party, or by the attacker, such as ransomware.
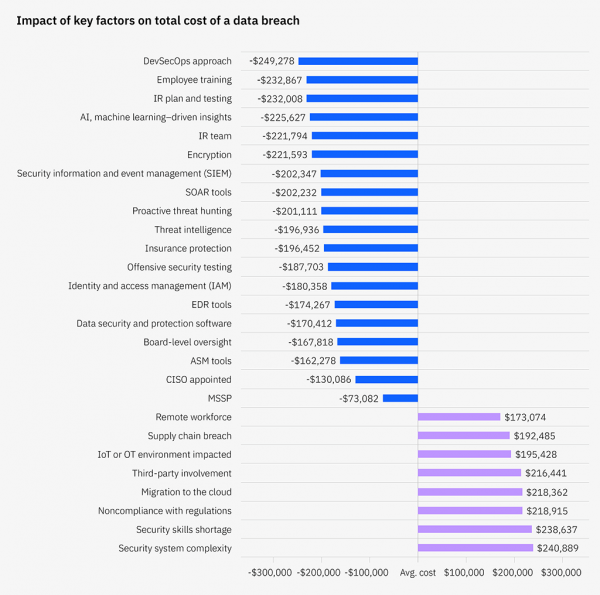 Breaches disclosed by attackers were not only the most expensive type of identifier – averaging $5.2 million per breach – they also took the longest to discover and contain, with a mean time of 320 days. Breaches identified internally cost $1 million less in comparison at $4.3 million and an average of 79 fewer days to contain at 241 days.
Breaches disclosed by attackers were not only the most expensive type of identifier – averaging $5.2 million per breach – they also took the longest to discover and contain, with a mean time of 320 days. Breaches identified internally cost $1 million less in comparison at $4.3 million and an average of 79 fewer days to contain at 241 days. - Key Cost Factors – The key factors associated with the biggest cost reduction in breaches included the adoption of a DevSecOps approach, employee training and incident response (IR) planning and testing. AI and encryption rounded out the top cost mitigators, all with cost savings of over $221K per breach.
- Malicious Attacks – Ransomware and destructive attacks were responsible for 24% and 25% of malicious attacks, respectively. Additionally, both attacks increased in costs by 13% from 2022, with ransomware costing $5.13 million and destructive attacks at $5.24 million per breach. While law enforcement saved time and money in containing breaches – 9.6% savings at $4.64 million per breach and 33 days less to contain – paying the ransom offered minimal savings.
- Security – Even as the global cost of a data breach increased, research participants were divided on security investments. 51% of respondents indicated they planned for additional security spending as a result of a breach.
- Solutions – The report recommended security practices to help organizations reduce the impacts of data breaches, which include:
- Building security into every stage of software development and deployment – testing regularly.
- Focusing on strong encryption, data security, and data access policies across the cloud.
- Using security AI and automation to increase speed and accuracy – Organizations with extensive use of security AI and automation identified and contained a data breach 108 days faster than organizations with no use.
- Practicing IR and understanding exposure to attacks most relevant to your industry and organization.
Bluefin believes in protecting your organization and your customer’s data with PCI-validated point-to-point encryption. Learn more about Bluefin, and download IBM’s report here.








